Automation Systems are transforming industries at an unprecedented pace. According to a recent report by McKinsey, companies that implement automation can improve productivity by up to 30%. These systems streamline various processes by minimizing human intervention. This advancement allows businesses to operate more efficiently and reduce operational costs.
However, the transition to Automation Systems is not without challenges. A survey by PwC reveals that 54% of workers express concerns over job displacement due to automation. This raises ethical questions about workforce adaptation and retraining. Organizations must address these issues to ensure a smooth transition.
In the manufacturing sector, Automation Systems have enhanced speed and accuracy. For example, robotic arms can perform tasks in a fraction of the time it takes a human worker. Still, reliance on these systems can lead to vulnerabilities. Cybersecurity threats pose risks that require careful consideration. Balancing efficiency and security is crucial in the evolving landscape of automation.
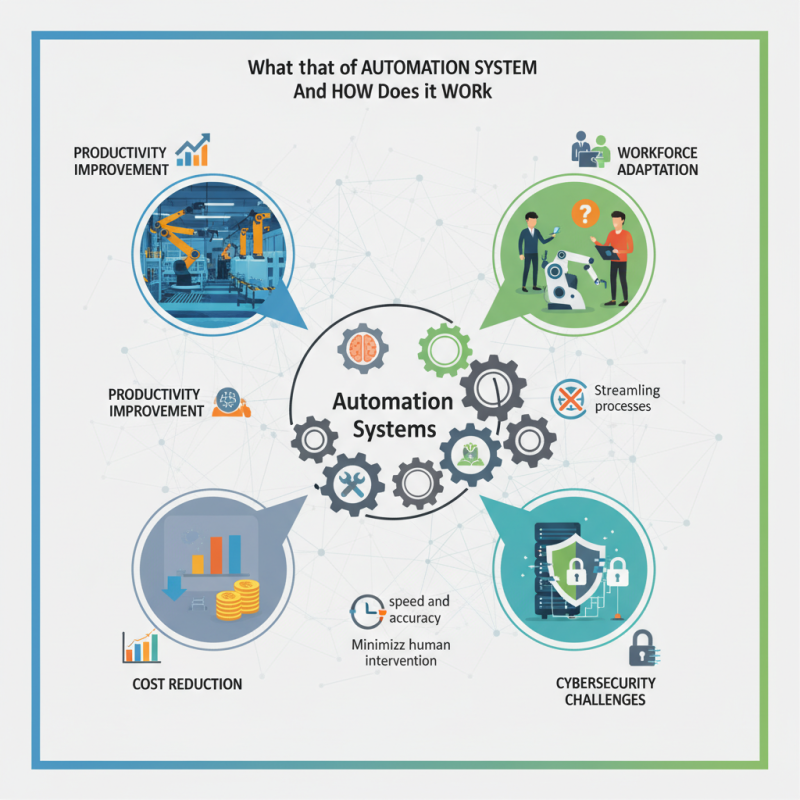
Automation systems are essential in various industries. They consist of key components that help streamline processes. These systems integrate hardware and software to enhance efficiency. Sensors, controllers, and actuators are crucial parts of any automation setup. Sensors detect changes in the environment. Controllers make decisions based on sensor inputs. Actuators physically carry out the commands.
Every automation system operates on the principles of feedback and control. Feedback informs the system of its current status. Control actions adjust operations to meet desired outcomes. For example, in a manufacturing plant, sensors monitor the speed of a conveyor belt. If it runs too fast, a controller signals to slow it down. This simple yet effective loop is foundational.
While automation systems offer many benefits, they are not without challenges. Implementing these systems requires careful planning. Mistakes can lead to inefficiencies or breakdowns. It's crucial to assess existing workflows. Adapting automation to them can be complex. Yet, observing how each component interacts is vital for improvement. Balancing innovation with practicality can be tricky but brings significant rewards.
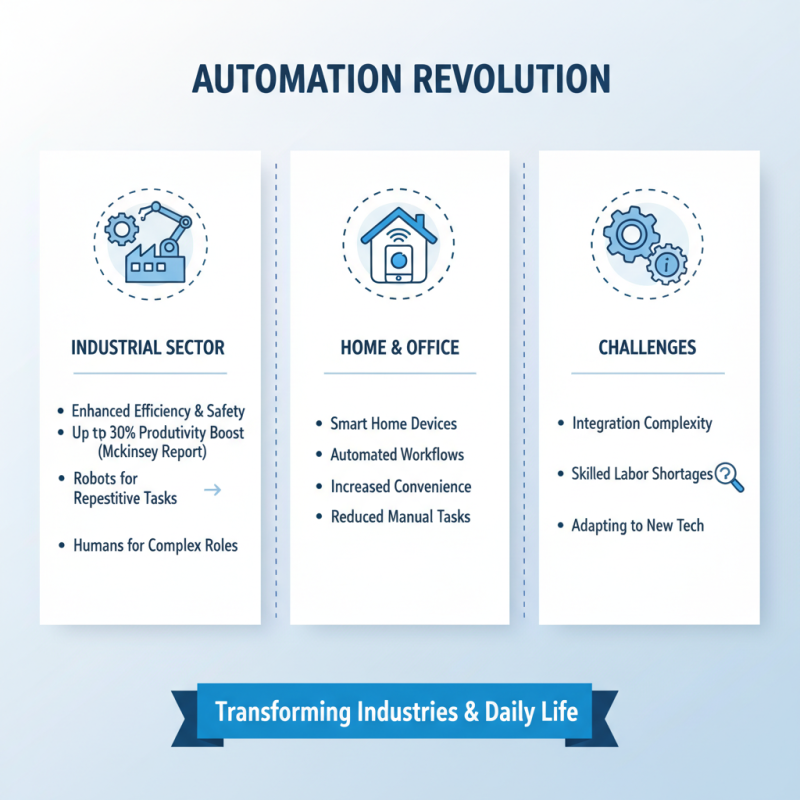
Automation systems are transforming various sectors, including industrial, home, and office applications. In industrial settings, automation enhances efficiency and safety. According to a report by McKinsey, companies that adopt automation can improve productivity by up to 30%. Robots can manage repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for complex roles. Yet, the integration can be challenging. Many businesses struggle with skilled labor shortages. Adapting technology requires a skilled workforce that is often hard to find.
Home automation is gaining traction as well. Market research indicates that the global home automation market is expected to reach $102.37 billion by 2025. Devices like smart thermostats and security systems offer convenience. However, concerns about cybersecurity arise with increased connectivity. Homeowners often overlook the risks involved. Implementing these systems requires education on potential vulnerabilities.
Office automation tools streamline communication and workflow. According to Statista, over 60% of organizations use some form of office automation. However, the reliance on technology can lead to complacency. Employees might struggle to adapt to new systems. Some may resist changes leading to decreased productivity. Balancing automation with human oversight is crucial for success.
Automation systems streamline numerous tasks. They harness various technologies to reduce human intervention. This results in improved efficiency and accuracy in processes. With sensors, control systems, and software, automation systems can optimize production flows. They track data in real-time, allowing for quick adjustments.
The integration of technologies is crucial. Machine learning algorithms analyze patterns in data. Programmable logic controllers automate machinery operations. Moreover, human operators oversee workflow. Their role is vital, as human intuition can solve unexpected issues. Yet, reliance on automation can sometimes lead to oversight in monitoring.
Processes are interconnected within an automation system. Each component must communicate effectively. If one part fails, it affects the entire operation. Regular assessments are necessary. This ensures that all systems function as intended. Communication, both between machines and between humans, often reveals flaws. Embracing continuous improvement can enhance overall efficiency.
| Dimension | Description | Example Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automation Type | Full Automation | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Increased efficiency |
| Control Systems | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) | SCADA systems | Real-time monitoring |
| Data Collection | Sensors and IoT Devices | Temperature sensors, smart meters | Improved data accuracy |
| Process Management | Workflow Automation | BPM software | Enhanced productivity |
| Integration | System Integration | API management tools | Seamless data flow |
Automation systems have revolutionized industries by improving efficiency and productivity. In manufacturing,
robotic arms take on repetitive tasks. This reduces human error and increases output. The swift movement of machinery minimizes downtime, allowing production lines to run smoothly.
However, reliance on automation can lead to workforce displacement, raising concerns about job security.
In healthcare, automation systems streamline patient management. Electronic health records facilitate better data management. Automated scheduling systems reduce wait times for patients.
Despite these benefits, some healthcare professionals worry about over-reliance on technology. Personal interactions can sometimes be lost, which is crucial in patient care.
The advantages of automation extend to logistics as well. Automated warehousing systems improve inventory management.
Drones and autonomous vehicles expedite deliveries. Yet, such advancements can create new challenges. Issues like cybersecurity and the need for constant maintenance arise.
Automation systems bring innovation, but they also require careful consideration of their broader impacts.
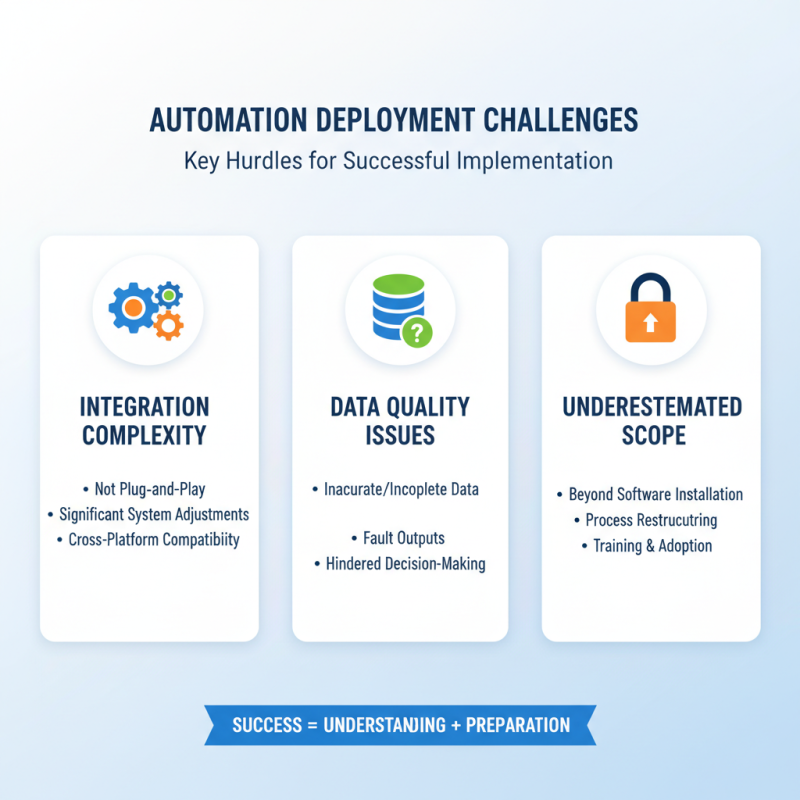
Deploying automation systems presents unique challenges. Understanding these hurdles is vital for successful implementation. Many organizations underestimate the complexity of integration. It's not as simple as plugging in software. Systems often require significant adjustments. Data quality issues can also arise. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to faulty outputs. This can hinder decision-making.
Consider this tip: conduct a thorough assessment of existing workflows before automation. Identify bottlenecks in current processes. Without this, automation can replicate inefficiencies. Another key consideration is team readiness. Employees may resist changes. They need proper training and support to adapt. Resistance can derail the automation project.
Reflect on your objectives. Are they clear and attainable? Ambiguous goals can lead to frustration. Engagement from all stakeholders is essential. Foster open communication. This builds trust and eases transitions. Remember, automation is a journey, not a destination. Mistakes will occur, and that's okay. Learn from them to improve your system continuously.






