In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation, optimizing your Dcs Control System has become crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and performance. According to the International Society of Automation (ISA), the implementation of advanced distributed control systems can lead to a significant reduction in operational costs, sometimes by as much as 20%. Furthermore, a report by Grand View Research indicates that the global market for Dcs Control Systems is expected to reach $25.21 billion by 2025, reflecting the increasing reliance on these systems for streamlined production processes across various sectors, including chemical, oil and gas, and pharmaceuticals.
The effectiveness of a Dcs Control System lies not only in its initial setup but also in its continual optimization. Studies show that organizations that regularly calibrate and update their control systems experience a 15% increase in overall productivity and a notable decrease in unplanned downtimes. As industries face pressure to improve their efficiency and reduce their carbon footprints, leveraging data analytics and advanced algorithms within Dcs Control Systems has become essential. This introduction of smart technologies not only enhances system performance but also aligns with sustainability goals, making it imperative for businesses to prioritize optimization strategies in their operational frameworks.

Distributed Control Systems (DCS) are pivotal in modern industrial automation, facilitating precise control over complex processes. Understanding the basics of DCS is essential for maximizing efficiency and performance in any operational environment. At its core, a DCS comprises a network of controllers, sensors, and actuators that work collaboratively to monitor and manage production processes. These systems utilize a hierarchical architecture, which allows for localized control while providing a comprehensive overview of the entire operation. This structure helps in reducing response times and enhances the reliability of process management.
The fundamental components of a DCS include the human-machine interface (HMI), control modules, and field devices. The HMI allows operators to interact with the system, providing real-time data visualizations and control options. Control modules execute algorithms to maintain set points and respond to disturbances, while field devices like sensors and actuators carry out the necessary adjustments in physical processes. Recognizing the interplay between these components is crucial for troubleshooting and optimizing performance, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and effectively in various conditions.
| Parameter | Description | Recommended Value | Measured Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Time taken for the system to respond to a change | < 2 seconds | 1.5 seconds |
| Control Loop Stability | Ability to maintain a steady output in response to disturbances | > 95% | 93% |
| Energy Consumption | Total energy used by the DCS system | < 100 kWh/day | 120 kWh/day |
| Data Latency | Delay in data transmission within the system | < 100 ms | 90 ms |
| System Uptime | Percentage of time the DCS system is operational | > 99% | 98% |

Identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for optimizing a Distributed Control System (DCS) to achieve maximum efficiency and performance. In the context of DCS, KPIs can encompass various metrics such as system response time, control loop performance, and overall plant efficiency. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, effective monitoring of these KPIs can lead to a reduction in operational costs by up to 20%. This highlights the significance of having a clear understanding of which indicators matter most in driving performance improvements.
To optimize a DCS, it is crucial to establish relevant KPIs tailored to specific operational goals. For instance, monitoring the energy consumption per unit of production can assist in identifying inefficiencies and provide actionable insights for energy management strategies. Additionally, metrics related to equipment uptime, such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time to Repair (MTTR), are critical for maintaining high availability and reliability of the system. A study by the Center for Business Practices indicates that organizations focusing on these KPIs experience an average increase of 15% in production efficiency. By systematically analyzing these indicators, operators can not only enhance performance but also make informed decisions regarding process improvements and resource allocation.
Enhancing the efficiency of control algorithms is crucial for optimizing a DCS (Distributed Control System) and achieving peak performance. One effective technique is to adopt model predictive control (MPC) strategies. MPC utilizes predictive models of the system to foresee future events and adjust control actions accordingly. By integrating real-time data and system dynamics, this approach allows for proactive adjustments, leading to decreased energy consumption and increased system stability.
Another important method involves fine-tuning PID (Proportional, Integral, Derivative) control parameters. Achieving the right balance in these parameters can significantly improve the system's response time and reduce oscillations. Tools like software simulators can help engineers test various configurations in a controlled environment, allowing them to identify the most effective settings without risking operational integrity.
Additionally, implementing advanced data analytics can help in monitoring system performance continuously. By analyzing historical data and identifying trends or patterns, engineers can make informed decisions on adjustments to the control algorithms. The incorporation of machine learning techniques may further enhance this by allowing the system to learn from past performance and optimize control decisions autonomously, thus enabling a more responsive and efficient DCS environment.
This chart illustrates the efficiency percentage of various optimization techniques applied to DCS control systems over a year. The data shows how different strategies enhance performance.
Regular maintenance and calibration of Distributed Control Systems (DCS) are essential practices that significantly enhance system efficiency and performance. According to a report by the International Society of Automation (ISA), failing to perform regular maintenance could lead to an increase in downtime, with unplanned outages costing companies an average of $260,000 per hour. To mitigate these risks, organizations should establish comprehensive maintenance schedules and follow best practices that involve routine checks on system parameters and regular software updates.
Calibration plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance of DCS equipment, affecting everything from control accuracy to process stability. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends that control systems be calibrated at least once a year, but more frequently for facilities operating in high-demand environments. Data shows that companies implementing a rigorous calibration protocol can enhance process efficiency by up to 15%, directly impacting the bottom line. By prioritizing these maintenance and calibration strategies, organizations can maintain not only the functionality of their DCS but also the overall safety and productivity of their operations.
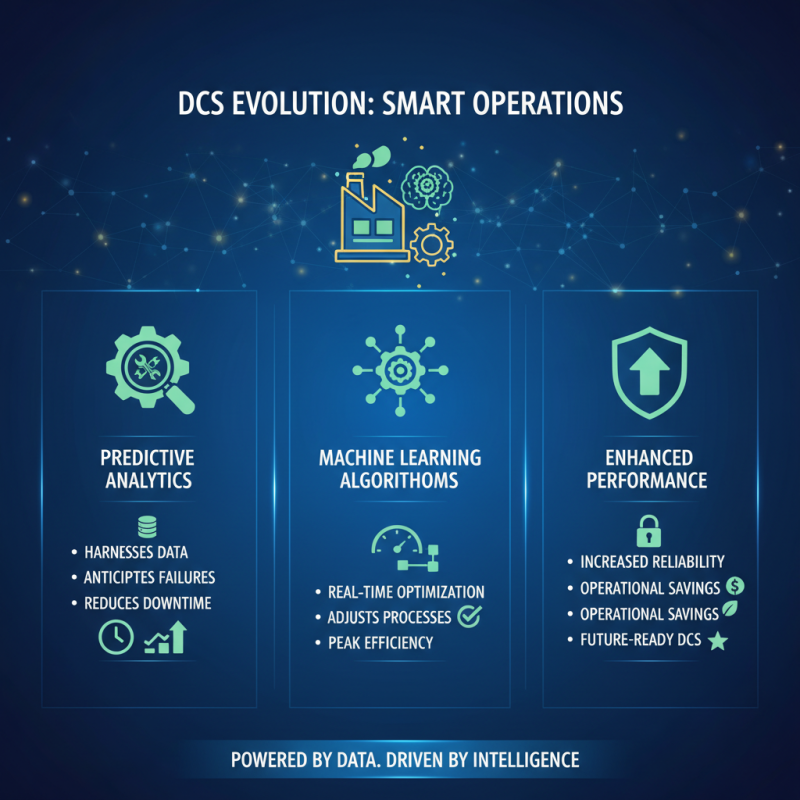
Integrating advanced technologies into your Distributed Control System (DCS) can significantly enhance performance and increase efficiency across your operations. One critical area of focus is the implementation of predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms. By harnessing vast amounts of historical and real-time data, these technologies can predict equipment failures before they occur, enabling timely maintenance and reducing downtime. Furthermore, such systems can optimize operational parameters dynamically, ensuring that processes run at peak efficiency based on the current conditions.
Another key aspect is the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices that provide real-time monitoring and greater visibility into the entire control system. IoT sensors can track everything from temperature and pressure to flow rates, contributing valuable data that can be analyzed for immediate insights. When combined with advanced visualization tools, operators and engineers can better understand system performance, identify bottlenecks quickly, and adjust operations in real-time, thus promoting a more responsive and agile system overall. Embracing these technologies not only drives operational excellence but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the organization.