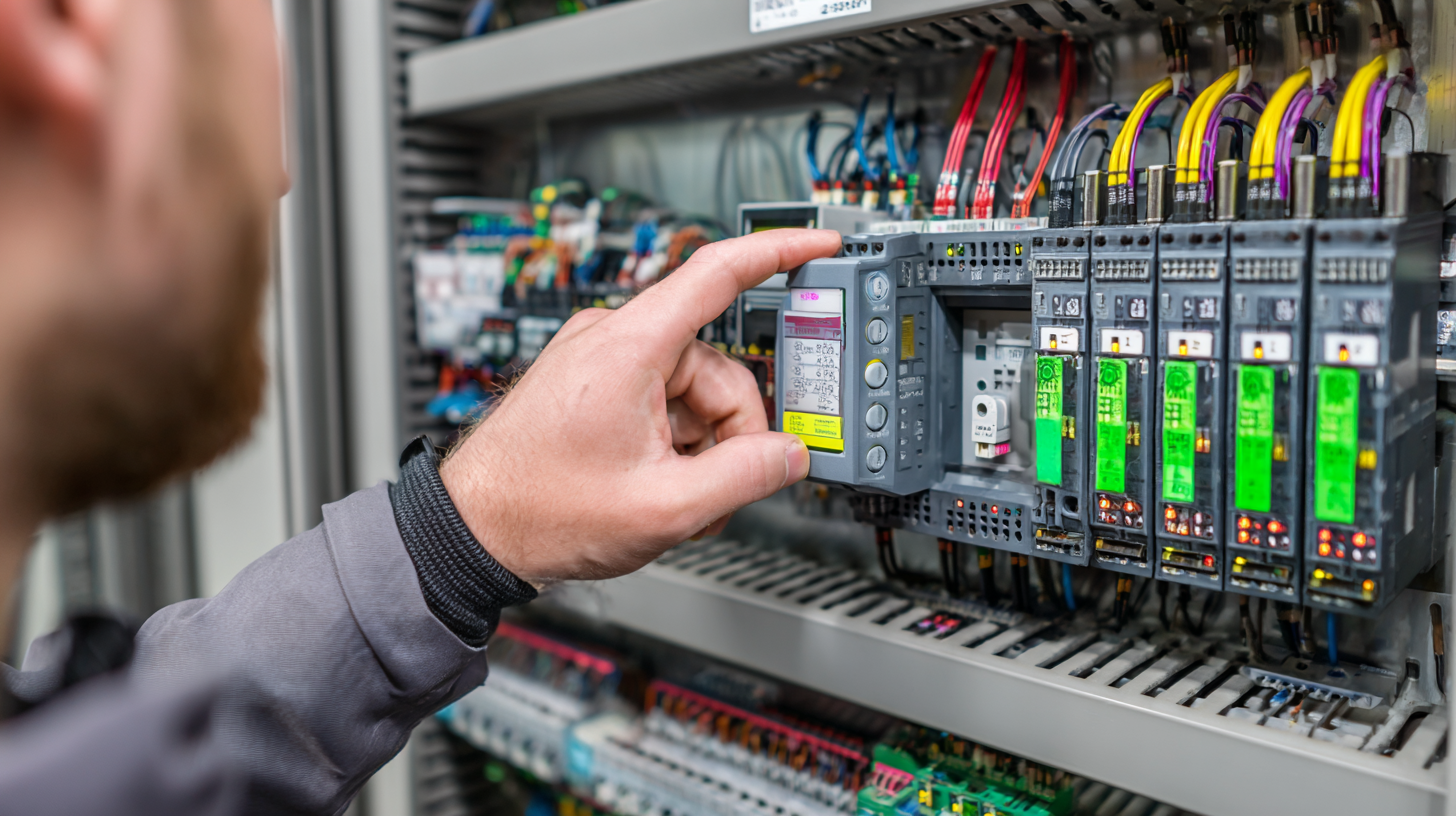
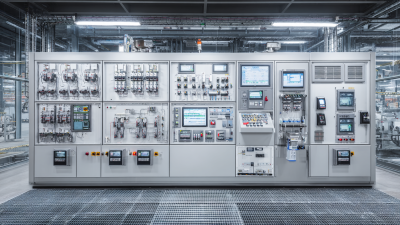
In the landscape of modern industrial automation, the PLC controller stands as a pivotal innovation that is transforming operations across various sectors. A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a specialized computer used for automation of electromechanical processes, which include control systems for machinery on factory assembly lines, amusement rides, or light fixtures. By enabling real-time monitoring and control, PLC controllers streamline processes, enhance precision, and increase efficiency. This article explores how PLC controllers not only simplify complex operations but also integrate seamlessly with digital technologies, exemplifying a new era of automation that is both intelligent and adaptive. As industries continue to embrace automation, understanding the integral role of PLC controllers becomes essential to unlocking the full potential of advanced manufacturing systems.
A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is a rugged digital computer widely used for industrial automation. It is designed to control manufacturing processes or machinery on factory floors, assembly lines, and other industrial environments. Unlike traditional computers, PLCs are built to withstand harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures, dust, and moisture. This resilience makes them essential for operations that require high reliability and uptime.
The primary function of a PLC is to monitor input signals from various sensors and devices, process the data using a pre-programmed logic, and then execute commands to control outputs, such as motors, valves, and lights. This automation allows for improved efficiency, precision, and safety in industrial settings. With programmable software, operators can easily modify the control processes, enabling quick responses to changing production needs. As the backbone of modern industrial control systems, PLCs have revolutionized automation by delivering adaptable, scalable, and efficient solutions across diverse industries.
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is essential in modern industrial automation, consisting of key components that work harmoniously to optimize production processes. At the heart of a PLC is the CPU (Central Processing Unit), which executes the control logic that dictates the behavior of machinery. According to a recent survey by MarketsandMarkets, the global PLC market is expected to reach $15.17 billion by 2026, highlighting the growing reliance on these devices in various industries.
Input/Output (I/O) modules are another critical component of PLCs, providing the means to interface with the machinery and processes being controlled. These modules convert the signals from sensors, switches, and other devices into a format the CPU can read and vice versa, allowing it to send commands to actuators and other outputs. A report by ResearchAndMarkets indicates that the increasing need for automated control systems is driving demand for advanced I/O configurations, including digital and analog types, enhancing the versatility and functionality of PLCs in diverse manufacturing environments.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) have become essential in modern industrial settings, playing a crucial role in streamlining processes. These robust devices are designed to automate tasks that require precision and reliability, such as assembly line operations, machine control, and data collection. By replacing traditional relay-based control systems, PLCs provide greater flexibility and scalability. They allow manufacturers to easily customize their operations, quickly adapting to changes in production demands or workflows.
In addition to improving efficiency, PLCs enhance communication across various machinery and systems. Their ability to process vast amounts of data in real time enables seamless interaction between different components of an industrial setup. This interconnectedness not only optimizes performance but also facilitates predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. As industries continue to embrace automation, the impact of PLCs in refining productivity and reducing errors cannot be overstated, making them a cornerstone in the advancement of industrial automation.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are integral to modern industrial automation, offering numerous benefits that drive efficiency and productivity in manufacturing environments. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global PLC market is projected to reach $12.24 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5%. This surge emphasizes the critical role PLCs play in reducing operational costs and enhancing process reliability.
One of the significant benefits of implementing PLC controllers is their ability to streamline complex automation processes. Unlike traditional control systems, PLCs enable real-time monitoring and control of machinery, which results in improved accuracy and reduced downtime. For instance, a study from ARC Advisory Group indicates that companies that adopted PLC technology experienced up to a 30% increase in production efficiency. Moreover, with their modular design, PLCs can easily be scaled and customized to fit various industries, from automotive to food processing, making them a versatile choice for manufacturers aiming to optimize their operations.
Additionally, PLC controllers contribute to enhanced safety and compliance in industrial environments. By automating critical safety functions and enabling better data management, firms can minimize risks associated with human error and ensure adherence to regulatory standards. According to a survey conducted by Automation World, around 85% of industrial users reported a significant improvement in safety and compliance metrics after integrating PLC systems into their operations. This highlights the transformative impact of PLC technology on both operational efficiency and workplace safety.
The evolution of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in industrial automation is marked by significant advancements in technology, leading to greater efficiency and flexibility in manufacturing processes. With the rise of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), modern PLCs are now equipped to handle vast amounts of data, allowing them to seamlessly integrate with various devices and systems. This integration not only enhances real-time monitoring and control but also fosters predictive maintenance, resulting in reduced downtime and operational costs.
Tips: When considering the adoption of PLC technology, prioritize systems that support interoperability with existing equipment. This adaptability is essential for a smooth transition to more advanced automation solutions.
Moreover, the future trend of using artificial intelligence within PLCs is set to revolutionize the industry. AI capabilities can analyze operational patterns, optimize performance, and even self-correct anomalies, thus taking automation to unprecedented levels. As industries increasingly turn towards smart manufacturing, embracing these emerging technologies will be crucial for maintaining competitive advantages.
Tips: Stay informed about emerging trends in PLC technology, as continuous learning can help businesses adapt to innovative practices and stay ahead in the market.